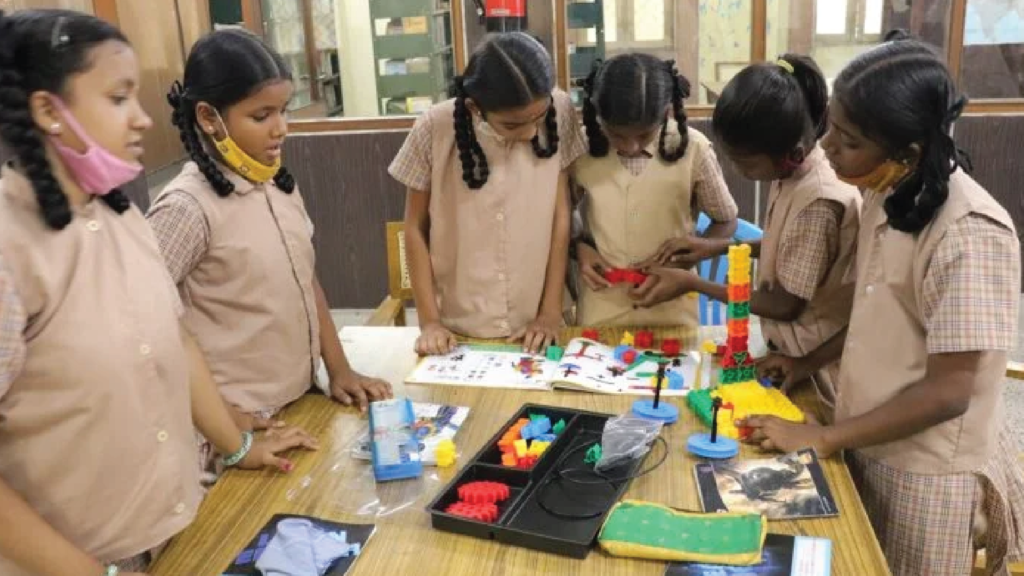
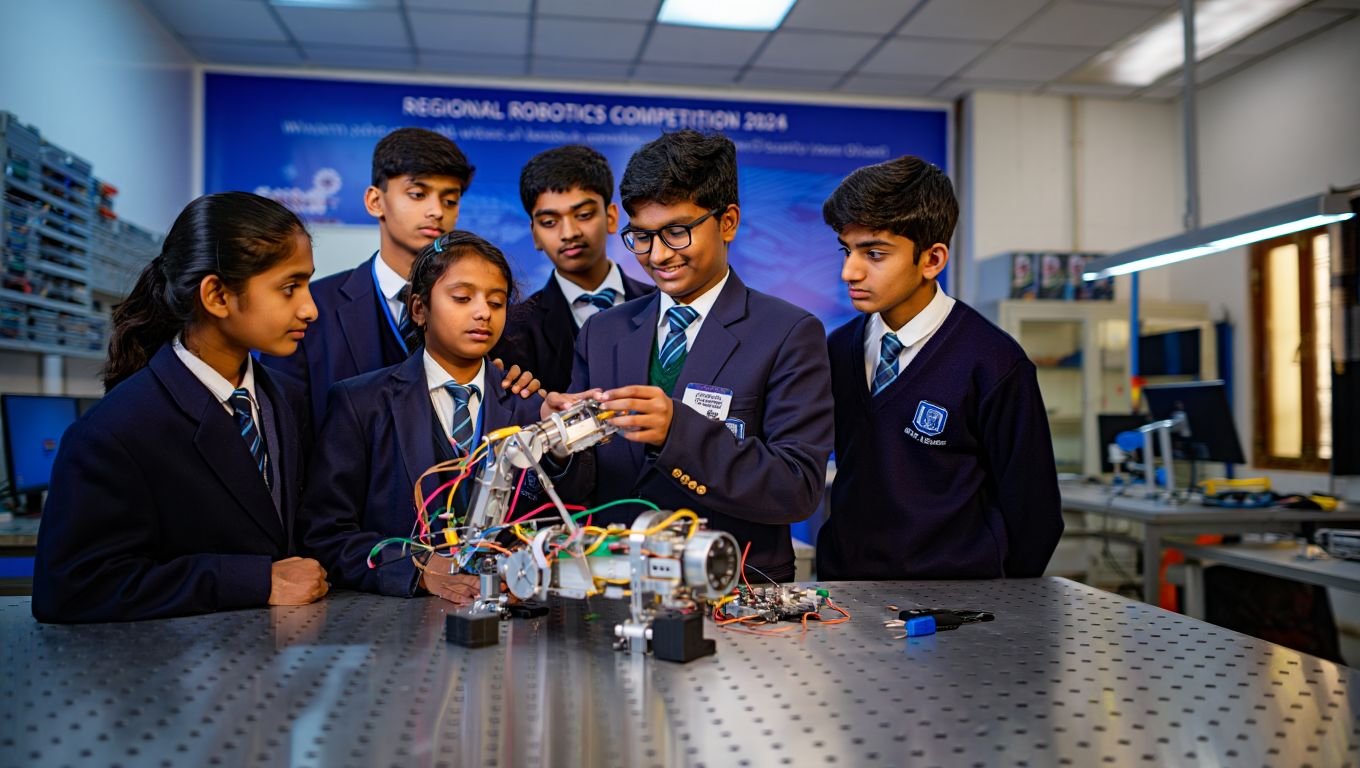
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in education in India has become a critical avenue for businesses to contribute to societal development and address educational inequities. With the enactment of the Companies Act 2013, which mandates eligible companies to invest in CSR, there has been a significant increase in corporate initiatives aimed at improving educational outcomes. Companies are actively involved in building and upgrading school infrastructure, providing scholarships, enhancing teacher training, and integrating technology into classrooms. These efforts are particularly impactful in rural and underserved areas, where access to quality education is often limited. By aligning CSR activities with educational goals, businesses are playing a pivotal role in fostering a more educated and skilled workforce, essential for India’s long-term economic growth and social progress.
Definition and Scope of CSR
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in India refers to the efforts made by companies to contribute to societal goals, particularly those related to sustainable development and social welfare. Mandated by the Companies Act, 2013, CSR requires companies of a certain size to allocate a portion of their profits to social initiatives. These efforts range from environmental sustainability projects to education, healthcare, and rural development.
Corporate Responsibility in Education
In the context of education, CSR initiatives aim to improve access, quality, and infrastructure. Companies are increasingly focusing on enhancing STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education to equip the younger generation with the skills needed for future job markets. This includes building schools, providing scholarships, developing digital learning platforms, and training teachers. By investing in STEM education, corporations not only fulfill their social responsibility but also help create a skilled workforce, driving economic growth and innovation in the long term.
The State of STEM Education in India
STEM education in India is undergoing significant transformation, driven by government initiatives and private sector participation. With over 250 million students enrolled in schools, India has one of the largest education systems globally. The government has launched programs like Atal Tinkering Labs and the National Education Policy 2020, emphasizing critical thinking and hands-on learning in STEM fields. Despite these efforts, challenges persist, including inadequate infrastructure, teacher shortages, and rural-urban disparities. However, the increasing involvement of tech companies and startups in education technology is helping bridge gaps, offering innovative solutions and digital resources to enhance STEM learning across the country.
Current Challenges and Opportunities for STEM in India
The country’s overall growth and economic prosperity depend heavily on education. The future of India is significantly shaped by STEM education. One strategy to generate a large number of scientists and engineers is STEM education. Science and technology have advanced in civilization with the passing of time. Science and technology coexist in the environment; technology is one such item that is utilized by all. The COVID-19 epidemic changed the way people used technology, making it necessary.
Infrastructure Deficiency: Many schools, especially in rural areas, lack basic infrastructure such as laboratories, libraries, and internet connectivity, essential for effective STEM education.
Teacher Shortages and Training: There is a significant shortage of qualified STEM teachers. Moreover, many existing teachers lack adequate training in modern STEM teaching methodologies and technologies.
Curriculum Rigor and Relevance: The STEM curriculum in many schools is outdated and lacks practical, hands-on learning experiences. This often leads to a lack of interest and engagement among students.
Gender Disparity: Societal norms and biases result in lower participation rates of girls in STEM fields. Encouraging female students to pursue STEM education remains a critical challenge.
Urban-Rural Divide: Students in rural areas have less access to quality STEM education compared to their urban counterparts, exacerbating educational inequities.
Students’ overall growth and development is aided by STEM education in India and other countries. It encourages pupils to think creatively. It also helps children become responsible citizens in society. Additionally, STEM education makes kids employable by teaching them critical skills for the future. Hence STEM education opens gates of opportunity for growth and development
Government Initiatives: Programs like Atal Tinkering Labs, STEM clubs, and the National Education Policy 2020 are promoting a more practical and inquiry-based approach to STEM education.
EdTech Revolution: The rise of education technology companies is providing innovative digital learning solutions, making quality STEM education more accessible and engaging.
Corporate CSR Involvement: Many companies are investing in STEM education as part of their CSR activities, focusing on infrastructure development, teacher training, and scholarships.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations between the government, private sector, and non-profit organizations are creating new models for delivering STEM education, especially in underserved areas.
Increased Focus on Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Initiatives to foster a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship among students, such as hackathons and innovation challenges, are gaining momentum, encouraging practical application of STEM knowledge.
Addressing these challenges and leveraging these opportunities can significantly enhance the quality and reach of STEM education in India, ultimately contributing to the country’s scientific and economic advancement.
CSR Initiatives in STEM Education
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives in STEM education in India have seen significant contributions from various companies aiming to bridge the educational gap. For instance, Tata Technologies launched a program to upgrade over 150 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) across multiple states, focusing on advanced manufacturing technologies and digital skills. Similarly, Infosys Foundation has been actively involved in setting up science centers and providing infrastructure support to schools in rural areas. Another notable example is IBM’s STEM for Girls initiative, which aims to empower over 200,000 girls across India with STEM skills through a combination of training and mentorship. These initiatives reflect the growing trend of corporate entities investing in the education sector, particularly in STEM, to foster a more skilled and innovative future workforce.
Major Corporate Players and Their Contributions
Major corporate players in India are making significant contributions to STEM education through various initiatives. Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) provides digital learning solutions and workshops via its TCS iON program, enhancing digital literacy among students. Infosys Foundation builds science centers and supports infrastructure and teacher training, particularly in rural areas. IBM India’s “STEM for Girls” initiative empowers over 200,000 girls with STEM skills through training and mentorship. Microsoft India’s programs like “Aspire Schools” and “Youth Spark” focus on digital skills and teacher training, impacting thousands of students and educators. Tata Technologies is upgrading over 150 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) with advanced manufacturing technologies. Google India nurtures coding skills through its “Code to Learn” contest and provides online STEM resources. These efforts collectively improve access to quality STEM education, preparing students for future technological advancements and fostering innovation.
Innovative Programs and Partnerships
Collaboration is one of the cornerstones of successful CSR in STEM education. Corporations can optimize their influence by collaborating with government agencies, non-profit groups, and educational institutions to pool their collective knowledge and resources. These partnerships and programmes make it easier to create and execute cutting-edge programs that cater to the changing requirements of both instructors and students.
Atal Innovation Mission (AIM):
- Initiative: Launched by the Indian government, AIM aims to create a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship across the country. It includes the establishment of Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs) in schools, where students can work on innovative projects using tools like 3D printers, robotics kits, and IoT devices.
- Partnerships: AIM collaborates with various educational institutions, corporate, and NGOs to provide resources, mentorship, and training.
- Impact: Over 5,000 ATLs have been set up across India, fostering a hands-on learning environment and encouraging students to develop problem-solving skills.
Intel AI for Youth:
- Initiative: Intel’s AI for Youth program aims to empower young students with AI skills, providing training in AI concepts, ethics, and applications.
- Partnerships: The program collaborates with the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) and several state governments.
- Impact: The initiative has trained thousands of students and educators, promoting AI literacy and preparing students for future AI-related careers.
Microsoft Imagine Academy:
- Initiative: Microsoft Imagine Academy provides a curriculum for students and educators to gain skills in Microsoft technologies, including cloud computing, AI, and data science.
- Partnerships: Collaborates with schools, colleges, and vocational institutes to integrate the curriculum into their programs.
- Impact: Equips students with industry-relevant skills, enhancing employability and preparing them for careers in technology.
Google’s CS Education Initiatives:
- Initiative: Google’s initiatives include programs like “Code to Learn,” offering students opportunities to develop coding skills, and “CS First,” a free computer science curriculum.
- Partnerships: Partners with various educational organizations and governments to implement these programs.
- Impact: These initiatives have reached thousands of students, fostering a strong foundation in computer science and programming.
IBM STEM for Girls:
- Initiative: IBM’s STEM for Girls initiative focuses on providing STEM education and career guidance to young girls, aiming to close the gender gap in technology fields.
- Partnerships: Collaborates with state governments and NGOs to implement the program in schools across India.
- Impact: The initiative has empowered over 200,000 girls with STEM skills, promoting gender diversity in STEM fields.
Tata Technologies and ITI Upgradation:
- Initiative: Tata Technologies has undertaken the project of upgrading Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) with advanced manufacturing technologies and digital skills training.
- Partnerships: Works in collaboration with state governments and educational institutions.
- Impact: The project aims to upgrade over 150 ITIs, significantly improving the quality of technical education and making it more relevant to industry needs.
EdTech Collaborations:
- Initiative: Various EdTech companies like BYJU’S, Vedantu, and Unacademy are partnering with schools and government bodies to provide digital learning solutions and resources.
- Partnerships: Collaborations include public-private partnerships to integrate digital learning tools into the traditional education system.
- Impact: These collaborations have expanded access to quality education, especially in remote and underserved areas, through interactive and engaging digital platforms.
Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) and TCS iON:
- Initiatives: TCS has been at the forefront with its flagship program “TCS iON,” providing digital learning solutions and conducting workshops to enhance digital literacy and STEM skills among students.
- Impact: Their programs have reached thousands of schools, improving the quality of STEM education and preparing students for the digital economy.
These innovative programs and partnerships are transforming STEM education in India by enhancing accessibility, improving the quality of education, and preparing students for future technological advancements and careers.
Impact of CSR on Future STEM Professionals
Corporate social responsibility in education is a calculated risk that pays off in the long run. Corporations have a crucial role to play in fostering the next wave of innovators who will propel technical developments and mold our future by promoting STEM education. Companies that engage in CSR activities receive benefits such as community goodwill, competitive difference, and consumer affinity. These benefits can come from financing STEM scholarships, offering internships, or encouraging a wider interest in STEM subjects. Companies may meet their social responsibility obligations and create a talent pool that is ready for the challenges of the twenty-first century by investing in STEM education. Because science and technology are the backbone of our economy, funding STEM education is essential for a better future.
Success Stories and Case Studies
Conclusion
CSR-based STEM activities in India represent a pivotal commitment by corporate entities towards fostering sustainable development and preparing the next generation of innovators and professionals. These initiatives not only address educational disparities and infrastructure gaps but also empower students with essential skills and knowledge
The Road Ahead for CSR and STEM Education
In 2024, the future goals for STEM in India focus on several key areas aimed at advancing education, innovation, and workforce development:
Enhanced Educational Access and Quality: Expand access to quality STEM education across all demographic segments, focusing on improving infrastructure, curriculum relevance, and teacher training. Initiatives like Atal Tinkering Labs and digital learning platforms will continue to play a crucial role.
Promotion of Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Foster a culture of innovation through initiatives like startup incubators, hackathons, and mentorship programs. Encourage entrepreneurship among students and researchers to drive technological breakthroughs and economic growth.
Gender Inclusivity in STEM: Address gender disparities by promoting greater participation of girls and women in STEM fields. Programs such as IBM’s STEM for Girls and scholarships targeting female students in STEM will be expanded to create a more inclusive workforce.
Integration of Emerging Technologies: Embrace emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain into STEM education and research. Collaborate with industry partners to ensure curriculum alignment with current and future technological trends.
Industry-Academia Collaboration: Strengthen partnerships between academia and industry to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills demanded by employers. Enhance internship opportunities, industry-sponsored research, and skill development programs.
Sustainability and Environmental Sciences: Emphasize STEM education and research in sustainable development and environmental sciences. Promote solutions addressing climate change, renewable energy, and resource conservation through interdisciplinary approaches.
Global Competitiveness: Prepare students to compete globally by aligning STEM education with international standards and fostering cross-border collaborations in research and innovation.
By focusing on these goals, India aims to nurture a skilled workforce capable of driving technological advancements, fostering innovation-led economic growth, and addressing global challenges through STEM-based solutions.
Future Prospects and Goals
In India, women’s chances in STEM fields appear bright. More chances for girls to seek jobs in STEM sectors will arise as long as the nation invests in STEM education and programs. In addition, a multitude of job opportunities for women are anticipated to arise due to the exponential growth in demand for competent workers in STEM fields. India is not only changing the lives of girls by empowering them via STEM education, but it is also laying the groundwork for a more prosperous and inclusive future.
When females in India are given equal opportunity to succeed in science, technology, engineering, and math, STEM education has the capacity to completely change their life. India is producing a generation of gifted and powerful women who will define the nation’s future by shattering gender stereotypes and encouraging girls to follow their talents in STEM fields. Girls in India may overcome obstacles and hurdles to create a more equitable and inclusive society with the help of parents, educators, and STEM education initiatives. By working together, we can empower girls and build a future in which all young women may excel in STEM professions and advance India’s growth.