The importance of STEM education—science, technology, engineering, and mathematics—cannot be emphasized in the quickly changing world of today. The need for an analytical, problem-solving, and critical-thinking skilled workforce has increased as we navigate an era characterized by technological innovation and globalization. This movement is picking up steam in India, where there is an increasing focus on incorporating STEM courses in India into the curriculum at all educational levels. This reform intends to equip students to address difficult social issues, such as digital transformation and climate change, in addition to improving their employability and preparing them for STEM jobs. The proliferation of STEM courses offers a viable avenue to promote innovation, creativity, and economic prosperity in the upcoming decades as the country embraces this educational revolution in STEM education in India.
The demand for a trained workforce in a world that is becoming more and more technology-oriented has led to a substantial shift in education, with STEM courses becoming more popular in India. Through its numerous STEM programs and projects, such as Tinkering Labs, the India STEM Foundation strives to provide children with the fundamental skills they need to succeed in STEM fields. This approach not only improves employability and encourages innovation, but it also equips students to take on difficult social issues like climate change and digital transition. India’s emphasis on critical thinking and practical applications makes it an ideal place to develop the next wave of leaders and innovators in the STEM sectors.
The India STEM Foundation is devoted to altering the educational landscape by encouraging excellence in STEM education in India through different STEM programs. Understanding how important STEM education is for fostering innovation and economic expansion, the foundation works to provide students with the tools they need to succeed in a world that is changing quickly. The India STEM Foundation develops young learners’ critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills via a variety of programs, including teacher training, experiential learning, and the creation of Tinkering Labs. By bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, the foundation is committed to empowering the next generation of innovators and leaders, ultimately contributing to India’s broader socio-economic development goals and increasing opportunities for STEM jobs in the future.
Current Landscape of STEM Education in India
A dynamic trend towards integrating science, technology, engineering, and mathematics into the core curriculum at all educational levels is reflected in the current state of STEM education in India. As the value of these disciplines in fostering innovation and economic expansion becomes more widely acknowledged, the number of STEM courses being taught in Indian schools, colleges, and universities has significantly increased. These courses cover everything from basic disciplines like physics and maths to more specialized areas like environmental engineering, robotics, data science, and artificial intelligence.
In order to create a more comprehensive educational framework, government efforts like the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 place a strong emphasis on the value of multidisciplinary methods and experiential learning. Through the creation of Tinkering Labs and teacher training initiatives, private institutions and organizations—such as the India STEM Foundation—are making a significant contribution to this transition. These initiatives seek to improve students’ problem-solving, critical thinking, and practical learning abilities while preparing them for careers in STEM.
STEM courses, including CSR programs, offered by India STEM Foundation:
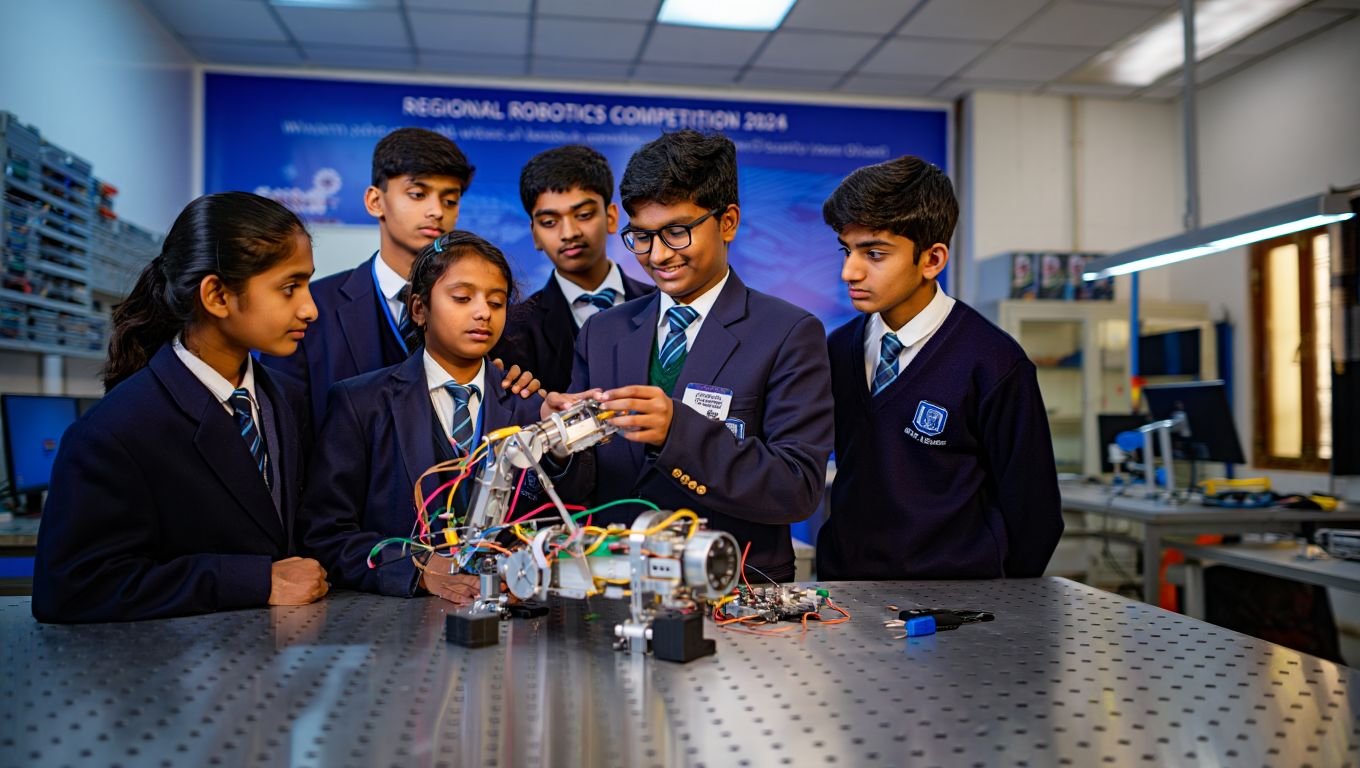
Tinkering Labs: Interactive educational environments that promote experimentation and discovery in a range of STEM subjects by allowing students to work on robotics, electronics, and coding projects.
Teacher Training Programs: To enhance STEM education in India, workshops and training sessions are designed to provide teachers with up-to-date teaching approaches, digital skills, and effective STEM pedagogy.
Gyanoday Program: An effort for supplemental education that gives kids in grades 9–12 extra aid in math and science to help them get ready for advanced STEM courses and competitive tests.
Anushikshan: A skill development program concentrating on professional skills for instructors and digital skills for pupils, including fields like data science, AI, and cybersecurity.
STEM Workshops & Camps: These are short-term programs intended to introduce students to STEM ideas through practical exercises, team-building exercises, and contests pertaining to different STEM courses.
Online learning resources: Having access to materials and courses that complement traditional education enables a wider audience to take STEM courses.
Community Engagement Initiatives: Programs designed to encourage participation from under-represented groups in STEM disciplines, foster inclusiveness, and increase local community knowledge of STEM education in India.
Factors Contributing to the Rise of STEM Courses in India
Economic Growth and Employment Demand: The swift advancement of India’s economy has resulted in a surge in the need for proficient experts in the fields of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Workers with these skills are becoming more and more necessary as industries change to spur innovation and keep businesses competitive, especially in STEM professions.
Government efforts: The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which emphasizes experiential learning and the integration of STEM courses into the curriculum, is one of the many efforts the Indian government has initiated in recognition of the significance of STEM education in India.
Technological Advancements: Data science, artificial intelligence, robots, and other professions have seen new prospects as a result of the digital revolution, which has completely changed industry. This change in the market pushes academic institutions to provide increasingly specialized STEM degrees.
Increasing Investment in Education: To raise the standard of STEM education and make it more accessible to students, the public and commercial sectors are making significant investments in educational infrastructure, materials, and teacher training.
focus on Research and Innovation: Academic institutions are placing an increasing amount of focus on research and innovation, creating a learning environment where students are motivated to solve problems and conduct scientific inquiry via practical projects and experiments.
Globalization: Indian students are competing more and more on a worldwide scale as the globe grows more linked. The need for high-quality STEM education in India that equips students for opportunities and difficulties faced by people throughout the world is driven by this global viewpoint.
Emphasis on Analytical Problem Solving and Critical Thinking: These abilities, which are essential to STEM courses, are being given more weight in today’s curriculum. This change equips students to take on challenging tasks across a range of disciplines.
Community & Extracurricular Programs: Students are encouraged to explore their interests outside of the regular classroom environment through programs like Tinkering Labs, seminars, and STEM contests, which improve engagement and cultivate a passion for STEM education in India.
The Future of STEM Education in India
The future of STEM education in India holds immense potential, driven by technological advancements, economic needs, and a growing recognition of the importance of STEM.
Technology Integration in Education: With the growing usage of digital tools, interactive software, and online learning platforms, students will have more flexible access to excellent resources for STEM education. For example, websites such as BYJU and Khan Academy provide interesting scientific and math information that encourages students to participate in STEM classes.
Emphasis on Interdisciplinary Learning: Multidisciplinary techniques that integrate ideas from many domains will be emphasized more and more in STEM programs in the future. For instance, the Atal Tinkering Labs program enables students to combine ideas from environmental science, robotics, and coding to produce products that tackle real-world problems.
Stress on Skill Development: As the labour market changes, a greater emphasis will be placed on providing students with real-world skills that are applicable to STEM careers. Courses such as Cisco Networking Academy offer hands-on training in networking and cybersecurity, preparing students for careers in technology.
Enhanced Industry Collaboration: Educational institutions and industry partnerships will proliferate, guaranteeing that curricula are in line with market expectations. For example, partnerships between academic institutions and businesses such as Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) give students access to internships and real-world project experiences, which improves their employability in STEM subjects.
Promotion of Research and Innovation: Academic institutions will place a higher priority on research and innovation in order to motivate students to work on initiatives that further science. As an illustration, the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) regularly supports student-led research projects in order to build an innovative and inquisitive culture.
To sum up, A rising dedication to including science, technology, engineering, and mathematics in the core curriculum is reflected in the state of STEM education in India today. The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and groups like the India STEM Foundation are supporting this effort, which focuses on helping students develop their critical thinking, problem-solving, and practical abilities. India is well-positioned to fulfill the needs of a fast-changing global economy by offering more and more specialized STEM courses and programs. This will eventually stimulate innovation and prepare students for successful careers in STEM employment.