Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics, or STEM education, is essential for educating pupils for the challenges of the contemporary world. It encourages students to investigate difficult ideas and apply theoretical knowledge in real-world contexts, which develops their critical thinking, problem-solving, and creative abilities. STEM education fosters creativity and flexibility in addition to providing pupils with the technical skills necessary for future employment. A solid foundation in STEM ensures that students are ready for a wide range of options in a work market that is changing quickly. As technology advances, a strong foundation in STEM helps students comprehend and manage new developments. In general, STEM education develops the abilities required to advance society and tackle global issues.
The incorporation of robotics into the educational curriculum has noteworthy advantages in terms of student engagement with STEM topics and the development of critical technical skills. The difficulties with this integration, though, include the lack of resources, the requirement for teacher preparation, and the necessity to integrate robots with the current curricular requirements. Achieving the full potential of robotics education requires properly addressing these difficulties. This article examines the challenges encountered with integrating robotics into educational initiatives and offers strategies for surmounting them. The essay seeks to assist educators and legislators in developing robotics programs that enhance the educational process by analyzing successful approaches and providing useful suggestions.
The Importance of Robotics in Education
Robotics is vital to education because it provides students with real-world, experiential learning opportunities that improve their comprehension of STEM subjects. As they design, construct, and program robots, students who work with robotics enhance their technical ability, creativity, and problem-solving abilities. Through experiential learning, abstract ideas become more relatable and concrete, leading to improved understanding and retention. Collaboration and cooperation are also fostered by robotics, and these are vital abilities for success in the workplace and in the classroom. By incorporating robots into the classroom, educators may help students become more innovative and prepare them for future jobs by giving them useful insights into engineering and technology. In general, robotics enhances the educational process and gives pupils vital abilities for the contemporary world.
Challenges in Integrating Robotics into the Curriculum
Including robots in the curriculum comes with a number of difficulties. Programs for robotics deployment may be limited by resource limitations, such as finance and equipment availability. Lack of professional development and training may cause problems for teachers, making it more difficult for them to teach robotics. It might be difficult to match robotics activities with current curricular standards; careful preparation and modification are needed. There is variation in student involvement; some students exhibit higher levels of ability and interest than others, which may have an impact on total participation. Furthermore, there are technological difficulties in maintaining and debugging robot equipment. In order to successfully integrate robotics education and maximize its benefits, it is imperative that these impediments be addressed.
The Foundation integrates robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) into its educational programs to prepare students for a world when these technologies will be commonplace.
Best Practices for Successful Integration
The following are essential best practices for effectively incorporating robotics into the curriculum at schools:
Professional Development: To increase instructors’ self-assurance and robotics proficiency, fund extensive training. It is important to offer materials and ongoing assistance to educators so they can keep up with the latest technology developments.
Curriculum Design: Create a flexible curriculum that complies with academic requirements and integrates robotics into a variety of courses. Make sure that, in order to improve learning results, robotics activities are smoothly incorporated into the current curriculum.
Resource Management: Obtain capital and assets via grants, collaborations, and neighborhood support. To guarantee the durability and efficacy of robotics equipment, establish a method for upgrading and maintaining it.
Student-Centric Approaches: Adapt robotics projects to suit the interests and skill levels of different pupils. To accommodate diverse learning styles and to promote active participation from all students, offer customized teaching.
Collaborative Learning: In robotics activities, emphasize cooperation and project-based learning. Fostering group work, idea sharing, and problem-solving among kids improves their ability to collaborate and communicate.
Continuous Evaluation: Utilising input from students, instructors, and other stakeholders, evaluate the robotics program’s efficacy on a regular basis. Make the required modifications and enhancements based on this input to keep the program engaging and current.
Implementing these best practices can help overcome challenges and ensure that robotics programs are effectively integrated into the curriculum, providing meaningful learning experiences and preparing students for future success.
India STEM Foundation
The Foundation gives students the tools they need to become the innovators and problem solvers of the twenty-first century through initiatives like Gyanodya and Anusikshan, among others.
The Gyanodya initiative is centred on giving children from underprivileged communities extra STEM instruction. Students are introduced to STEM ideas in an enjoyable and engaging way through interactive seminars, practical exercises, and mentorship sessions.
The Anusikshan program offers advanced STEM courses and enrichment activities to students in secondary and upper secondary education. These courses stress practical application, problem-solving techniques, and critical thinking skills in addition to standard classroom instruction.
Sanrachna, the organization, offers the necessary infrastructure—smart classrooms, libraries, solar power, and more—to transform educational establishments through the Sanrachna project.
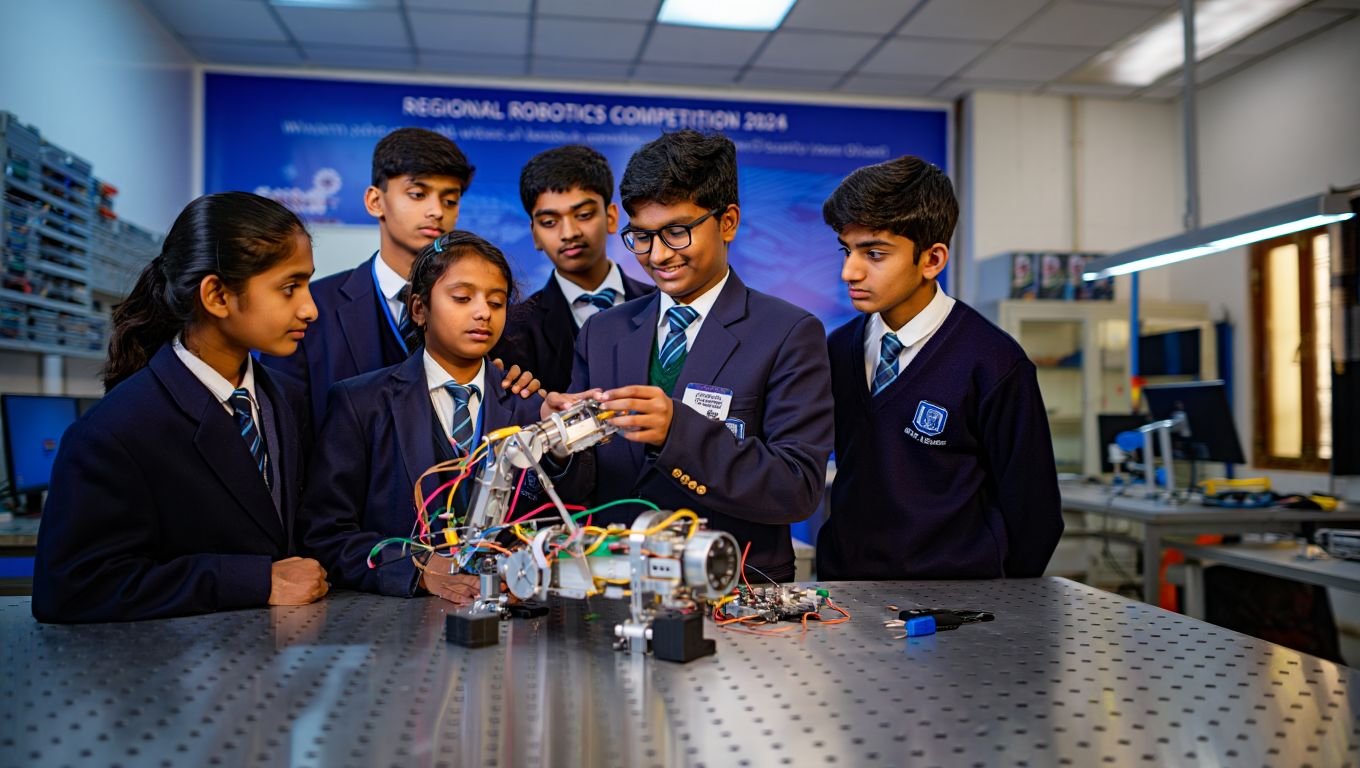
Robo Siksha Kendra: The Robo Siksha Kendra initiative aims to develop students’ interest in and proficiency in robotics by offering comprehensive training modules, state-of-the-art robotics facilities, and advanced robotics kits. Through hands-on learning experiences, students are exposed to a range of robotics concepts, including programming, circuit design, and mechanical engineering. One of the primary objectives of the Robo Siksha Kendra program is to enhance students’ critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration skills. Students who take part in robotics contests and projects improve their collaboration, analytical thinking, and application of STEM concepts to real-world scenarios.
Moreover, the curriculum aligns with the broader goals of the India STEM Foundation, which include fostering students’ technological literacy, inventiveness, and creativity.
The Robo Siksha Kendra program aims to reach students from a range of Indian communities and backgrounds by emphasizing accessibility and diversity. The India STEM Foundation collaborates with educational institutions, governmental organizations, and corporate sponsors to ensure that all students, regardless of financial status or geography, have access to robotics instruction.
In conclusion, by encouraging critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, STEM education is essential for equipping students to take on contemporary difficulties. This is improved by robotics, which gives students practical experience, sharpens their technical abilities, and gets them ready for the workforce. Learning results and student engagement may be greatly increased by integrating robots, even in the face of obstacles like curriculum alignment and resource limitations. Initiatives from the India STEM Foundation, such as Robo Siksha Kendra and Gyanodya, tackle these issues by offering tools, instruction, and hands-on training. When robotics is successfully incorporated into the classroom, it gives students the tools they need to be innovative and successful in a world that is changing quickly.