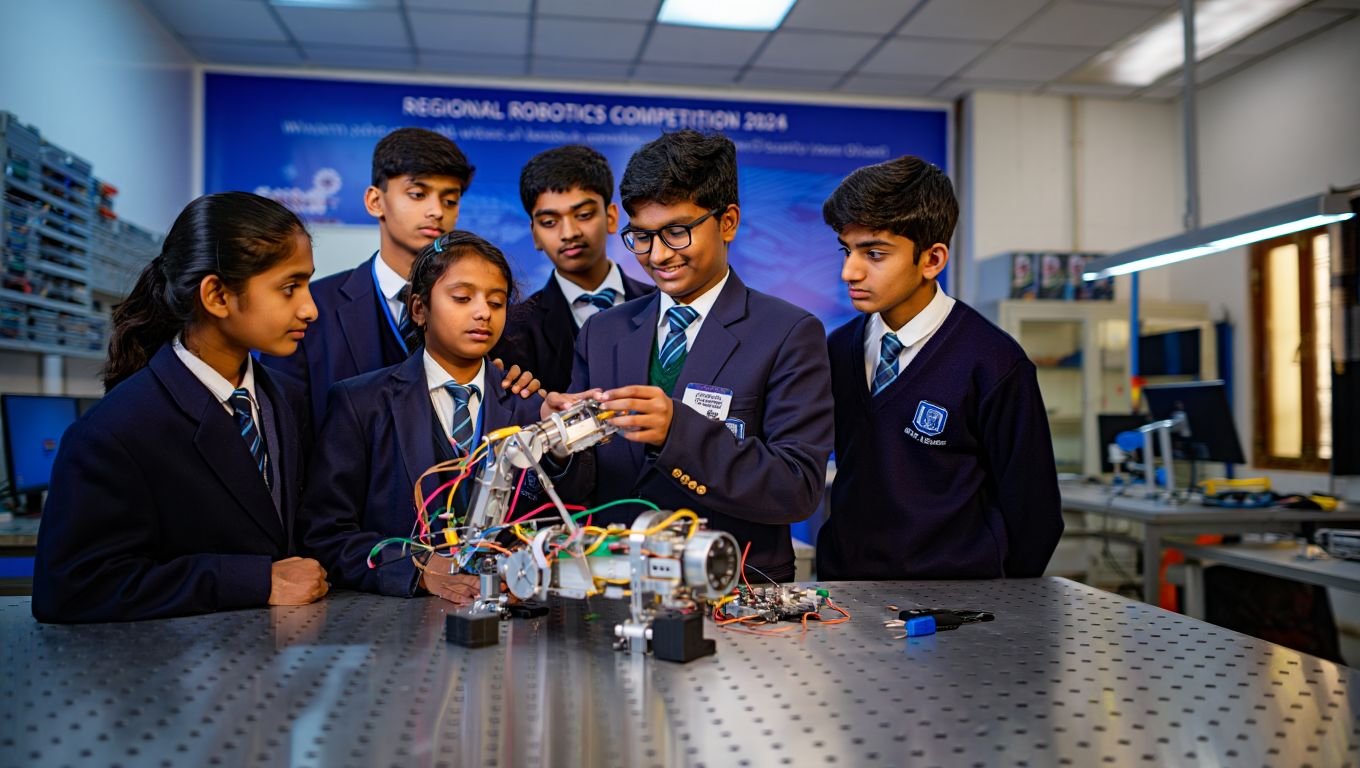
As we look to the future, the landscape of STEM education is evolving rapidly in response to technological advancements, changing workforce demands, and emerging educational paradigms. This article explores key trends and challenges shaping the future of STEM education and how stakeholders can adapt to meet the needs of tomorrow’s learners.
Emerging Trends in STEM Education
Integration of Emerging Technologies: Advances in technologies such as artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and robotics are transforming the way STEM subjects are taught and learned. Integrating these technologies into STEM curriculum can enhance engagement and provide immersive learning experiences.
Interdisciplinary Approaches: The boundaries between traditional STEM disciplines are blurring as interdisciplinary approaches gain traction. Emphasizing connections between science, technology, engineering, and mathematics fosters creativity and innovation and prepares students for careers in multidisciplinary fields.
Challenges Facing STEM Education
Equity and Access: Ensuring equitable access to quality STEM education remains a significant challenge, particularly for underserved communities and marginalized groups. Addressing disparities in resources, opportunities, and representation is essential for promoting diversity and inclusivity in STEM.
Preparing for the Future Workforce: Rapid technological advancements are reshaping the skills required for the workforce of the future. STEM education must adapt to equip students with the critical thinking, problem-solving, and digital literacy skills needed to thrive in a rapidly changing labor market.
Adapting STEM Education for the Future
Promoting Experiential Learning: Hands-on, experiential learning approaches are gaining popularity in STEM education as they provide students with real-world skills and experiences. Project-based learning, internships, and apprenticeships enable students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical problems.
Fostering Lifelong Learning Skills: In addition to technical skills, STEM education must prioritize the development of lifelong learning skills such as adaptability, resilience, and collaboration. Cultivating a growth mindset and a passion for continuous learning is essential for success in an ever-evolving world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of STEM education holds tremendous promise and potential, but also presents significant challenges. By embracing emerging trends, addressing equity issues, and fostering lifelong learning skills, we can ensure that STEM education remains relevant and impactful in preparing students for the opportunities and challenges of tomorrow.